Rack Server vs Tower Server: Which Is Right for Your Business?

Rack Server vs Tower Server: Which Is Right for Your Business?
Introduction: Why Your Server Choice Matters
As digital transformation accelerates across Egypt and the Middle East, businesses are relying heavily on stable, high-performance, and scalable IT infrastructure. Whether your organization is small, medium, or enterprise-grade, choosing the right server form factor is essential for long-term efficiency.

One of the most important decisions today is understanding the differences between server architectures, especially when comparing Rack Server vs Tower Server. This decision impacts:
(Performance, Scalability, Power usage, Space, Cost, Future expansion, System reliability)
This comprehensive guide provides a full enterprise comparison, showing when
a rack server is the better choice, when a tower server is more suitable, and how each impacts your operational efficiency.
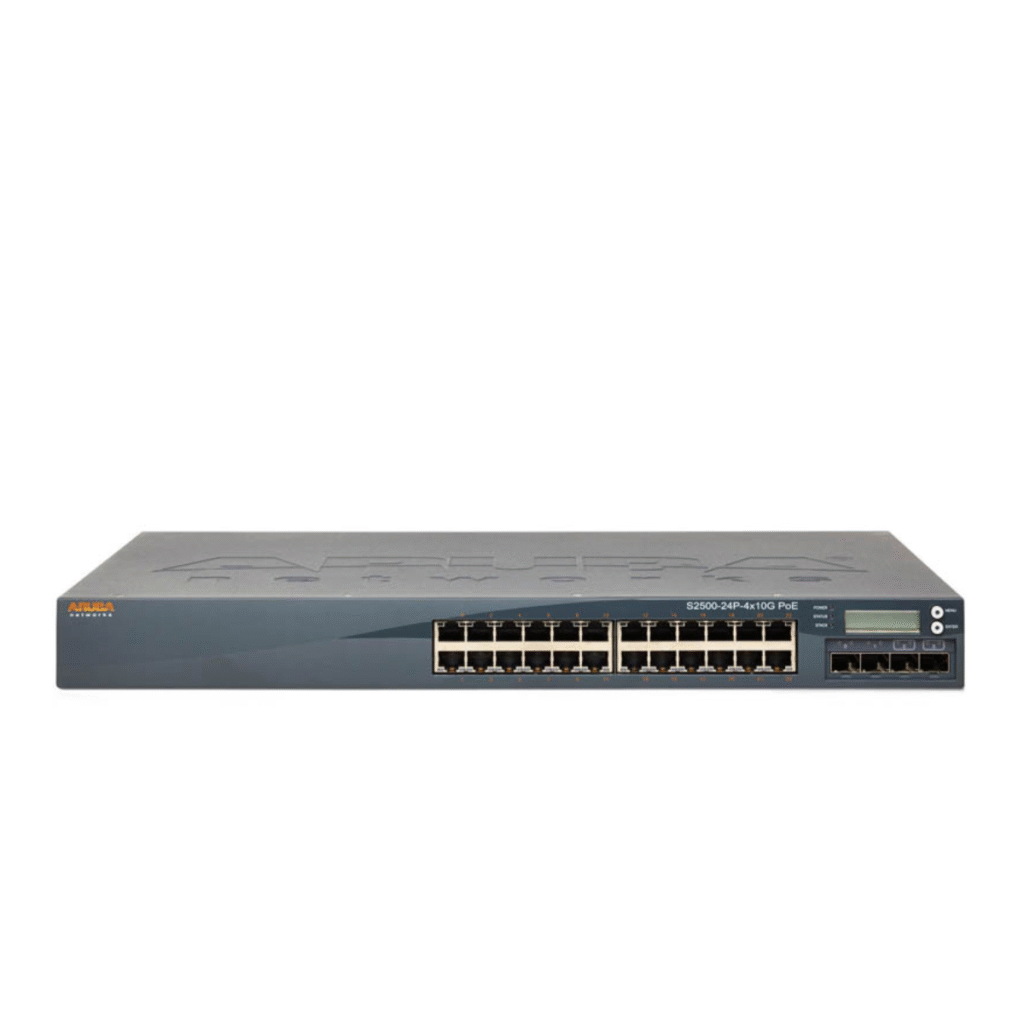
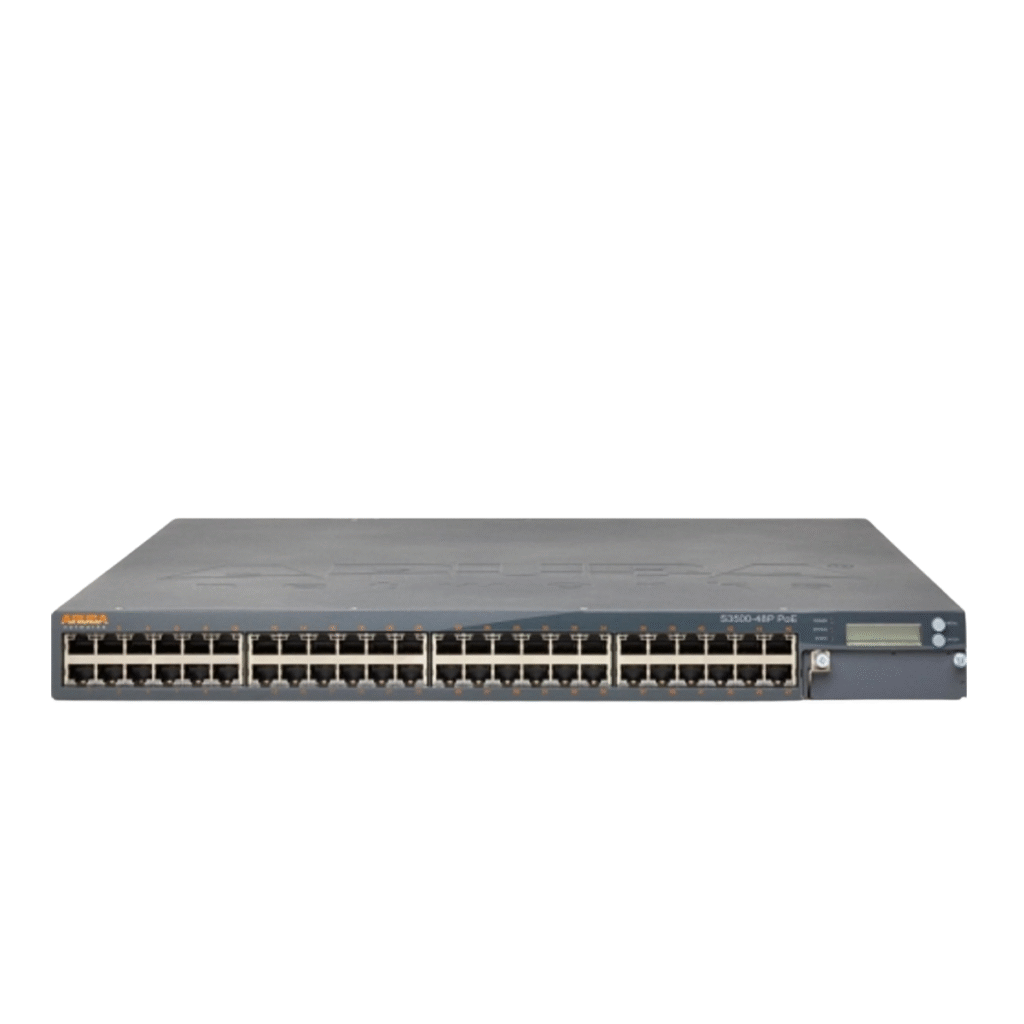
What Is a Tower Server? Full Technical Breakdown
Definition and Purpose
A Tower Server is a standalone, vertically oriented server designed to operate similarly to a desktop workstation but with enterprise-grade internal components.
It is ideal for small businesses or companies starting their first on-premise server deployment.

Tower Server Key Characteristics
Independent chassis with dedicated cooling
Quiet operation suitable for office rooms
Easy to deploy and manage
Lower power consumption
Supports multiple storage disks
Cost-effective initial investment
Tower servers are commonly used for file sharing, data backups, ERP, CRM, POS systems, and light virtualization.
Tower Server Architecture Explained
1. Chassis Design
The larger, vertically-oriented chassis provides excellent airflow and easier maintenance. It allows future upgrades in:
RAM
PCIe cards
Graphics accelerators
2. Cooling System
Tower servers use traditional air cooling with large, slow-speed fans — meaning:
Lower noise
Less vibration
Ideal for office use without a dedicated server room
3. Internal Storage
Tower servers often support several 3.5-inch HDDs, making them perfect for local storage solutions.
4. Power Efficiency
Because tower servers are not designed for extreme workloads, they consume less electricity — ideal for companies with limited operational budgets.
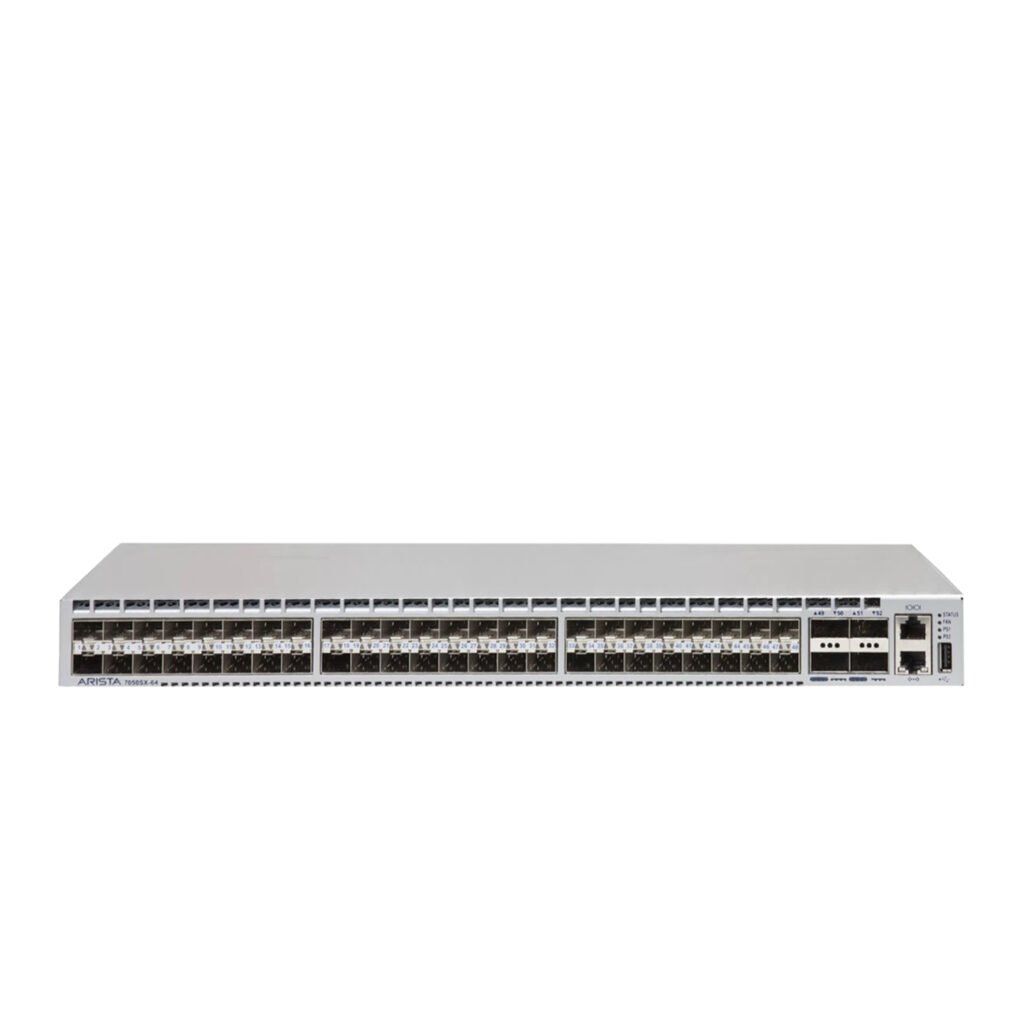
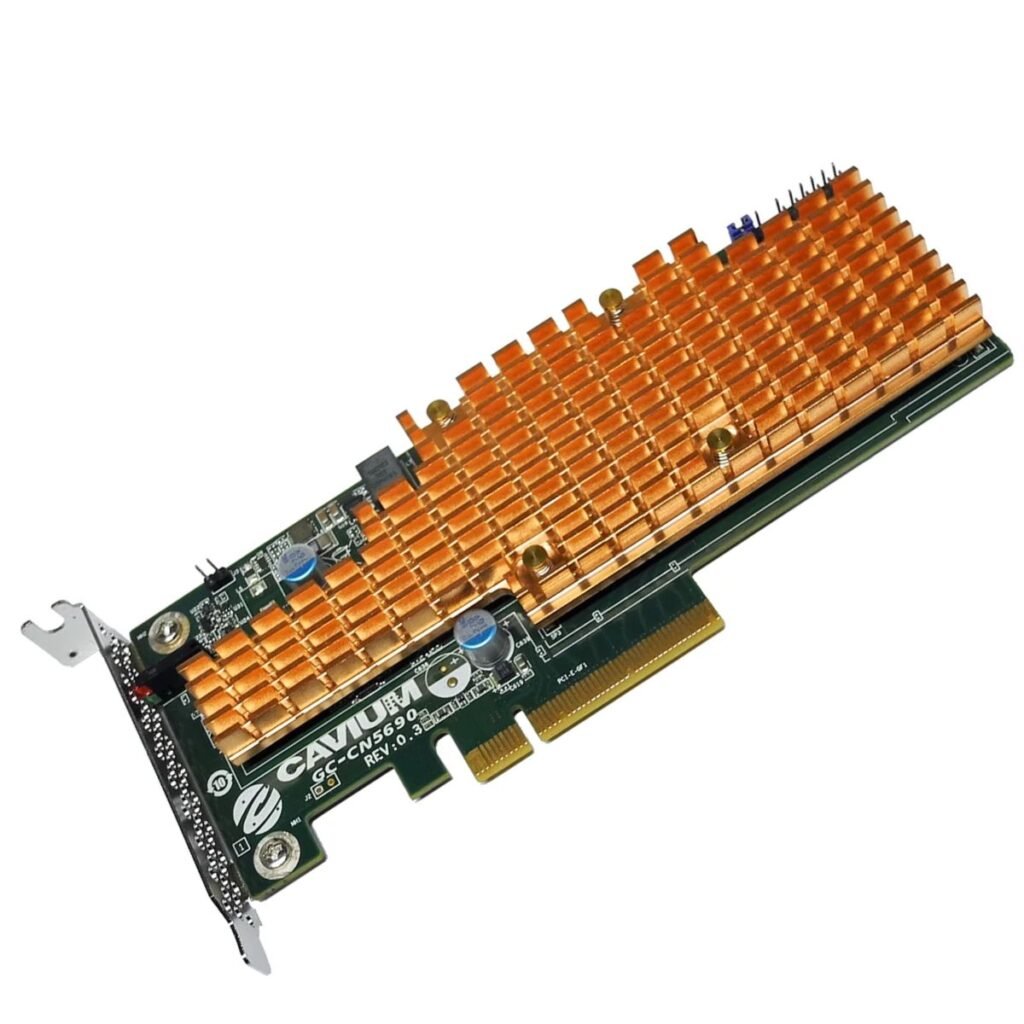
What Is a Rack Server? Enterprise-Level Explanation
Definition and Purpose
A Rack Server is a horizontally structured server designed to fit into a standardized rack cabinet. These servers come in sizes like 1U, 2U, and 4U and are built for high-density, high-performance computing.
Rack servers are used in:
Data centers
Telecom and ISP environments
Large enterprises
Virtualization clusters
Cloud deployments
AI and GPU workloads
Rack Server Key Characteristics
High-density performance
Centralized cable management
Excellent scalability
Designed for continuous heavy workloads
Full enterprise redundancy
Requires structured cooling
Rack Server Architecture Explained
1. Compact, High-Density Design
Their slim form factor fits into vertical rack cabinets, enabling hundreds of servers in a single room.
2. Enterprise Cooling
Rack servers use high-RPM fans and ducted airflow systems. They require a dedicated server room because:
They generate intense heat
They produce loud operational noise
They perform better in controlled cooling environments
3. Shared Infrastructure Compatibility
Rack servers integrate smoothly with:
SAN / NAS storage arrays
UPS power backup
Cooling systems
Network switches
Cable organizers
4. Superior Performance
Rack servers support:
Dual high-core CPUs
Massive RAM capacity
NVMe SSD arrays
Multiple GPU cards
High-bandwidth network interfaces
Rack Server vs Tower Server: Full Technical Comparison
1. Performance Comparison
Tower Server Performance
Best for small to medium workloads
Limited CPU and GPU support
Suitable for office operations and local apps
Rack Server Performance
Designed for maximum performance
Supports high-core CPUs and professional GPUs
Ideal for virtualization, databases, and enterprise workloads
Winner: Rack Server
2. Scalability and Growth Capability
Tower Server Scalability
Offers hardware upgrades
Limited by single-unit design
Not ideal for multi-server environments
Rack Server Scalability
Add servers simply by adding more rack units
Centralized management
Supports cluster deployments
Easily integrates with enterprise storage
Winner: Rack Server
3. Space and Physical Footprint
Tower Servers
Large chassis
Occupies desk or floor space
Hard to manage multiple towers
Rack Servers
Extremely space-efficient
Perfect for high-density deployments
Organizes servers neatly in one rack
Winner: Rack Server
4. Noise Level
Tower Servers
Very quiet
Suitable for offices
Rack Servers
Very loud due to high-RPM fans
Must be placed in a server room
Winner: Tower Server
5. Cooling Requirements
Tower Server Cooling
Light to moderate cooling
Naturally efficient airflow
Rack Server Cooling
Requires professional cooling
Designed for high heat loads
Winner:
Office → Tower
Data center → Rack
6. Power Consumption
Tower Servers
Lower power usage
More energy-efficient for small workloads
Rack Servers
Higher consumption but better performance-per-watt
Winner:
Tower Server (small businesses)
Rack Server (enterprise workloads)
7. Storage Capacity
Tower Servers
High number of 3.5” bays
Good for backup and file storage
Rack Servers
High-speed NVMe storage
Hybrid storage options
Winner:
High capacity → Tower
High speed → Rack
8. Cost and Budget Planning
Tower Server Costs
Lower upfront cost
Minimal infrastructure needed
No rack cabinet required
Rack Server Costs
Higher initial investment
Requires rack, cooling, structured cabling
Long-term savings per compute unit
Winner:
Tower Server (low budget)
Rack Server (long-term ROI)
Ideal Use Cases for Tower Servers
Small businesses (1–50 employees)
Clinics and pharmacies
Local file servers
POS and accounting systems
Small ERP solutions
Light virtualization
Backup/local storage server
Ideal Use Cases for Rack Servers
Data centers
Enterprises and large organizations
Virtualization clusters
Web hosting and cloud environments
AI training and GPU workloads
High-performance databases
Distributed infrastructures
Pros and Cons Summary
Tower Server Pros
Low cost
Less noise
Easy to manage
No rack required
Good storage capacity
Tower Server Cons
Takes up space
Limited scalability
Not ideal for heavy workloads
Rack Server Pros
Extremely scalable
High performance
Professional cable management
Redundant components
Ideal for virtualization and enterprise apps
Rack Server Cons
Requires dedicated cooling
Loud operation
Higher upfront cost
Final Decision Framework
Choose a Tower Server if your business:
Has limited space and no server room
Needs quiet operation
Has a small IT team
Requires cost-effective deployment
Handles light workloads
Choose a Rack Server if your business:
Plans for rapid growth
Requires high uptime
Uses virtualization or cloud environments
Has a server room or data center
Needs heavy processing power
Conclusion: Making the Right Investment
The debate of Rack Server vs Tower Server ultimately depends on your operational needs, long-term planning, and available infrastructure.
For small businesses needing simplicity:
Tower Server is ideal.
For enterprises needing scalability, performance, and redundancy:
Rack Server is the superior choice.
With digital transformation accelerating across Egypt, investing in the correct server form factor ensures system stability, strong performance, and future-proof infrastructure for your organization.